 每条队列规则,都有2个速率限制参数:
每条队列规则,都有2个速率限制参数:
- CIR (约定信息速率Committed Information Rate) – (在RouterOS中的参数为limit-at) 最坏的情况下,无论如何都会将得到给定的的CIR传输量(假设我们能发送那么多的数据量)。
- MIR (最大信息速率Maximal Information Rate) – (在RouterOS中的参数为max-limit) 最好的情况下,如果父级有剩余带宽,才能获得这部分剩下的带宽。
- CIR约定速率之和,即所有子队列CIR速率总和必须小于或等于可获得父级总流量。
CIR(parent)* ≥ CIR(child1) +...+ CIR(childN)
父级与主父级可以设置为 CIR(parent)=MIR(parent)- 任何子级的MIR最大速率必须小于或者等于父级的MIR最大速率
MIR (parent) ≥ MIR(child1) & MIR (parent) ≥ MIR(child2) & ... & MIR (parent) ≥ MIR(childN)
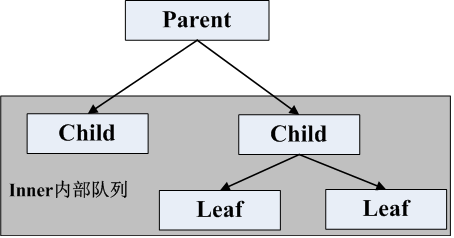
具体的HTB内容请参阅RouterOS入门到精通! 这里演示Parent定义为网络接口,区分上行和下行流量,外网WAN口作为出方向,定义为上行,内网LAN接口则作为下行,实例仍然通过HTB在Queue tree的配置标记不同类型的数据流,实现优先级的带宽控制。 注意:Parent基于网络接口配置,仅适用于单线接入和一个内网接口的网络! 首先查看接口上的IP地址:[admin@MikroTik] /ip address> print Flags: X, D - DYNAMIC Columns: ADDRESS, NETWORK, INTERFACE # ADDRESS NETWORK INTERFACE ;;; defconf 0 192.168.88.1/24 192.168.88.0 bridge 1 D 100.64.100.119/32 100.64.100.1 pppoe-out1在/ip address下看到有两个网络接口,一个是内网的bridge,一个是外网的pppoe-out1拨号接口。
基于协议的HTB
Queue tree里建立HTB等级流控,在mangle标记流量,首先提取TCP的80和443端口标记为web流量,然后将剩下的流量标记为other。 先是连接标记,匹配源地址是192.168.88.0/24的内网IP地址段,并提取tcp协议的80和443端口连接标记为web,然后web连接标记中提取数据包,标记为web,passthrough设置为no,不再下行传递。/ip firewall mangle add action=mark-connection chain=forward dst-port=80,443 new-connection-mark=\ web passthrough=yes protocol=tcp src-address=192.168.88.0/24 add action=mark-packet chain=forward connection-mark=web new-packet-mark=web \ passthrough=no最后是标记192.168.88.0/24剩下的连接,选择connection-mark=no-mark的连接,并从中提取数据包标记为other
/ip firewall mangle add action=mark-connection chain=forward connection-mark=no-mark \ new-connection-mark=other passthrough=yes src-address=192.168.88.0/24 add action=mark-packet chain=forward connection-mark=other new-packet-mark=\ other passthrough=no在queue tree创建HTB配置,首先创建父级队列down和up,分别对应上行的外网口pppoe-out1和下行的内网口bridge,出口总带宽是150Mbps,上行带宽80Mbps,上行和下行都预留一部分带宽,用于缓冲。
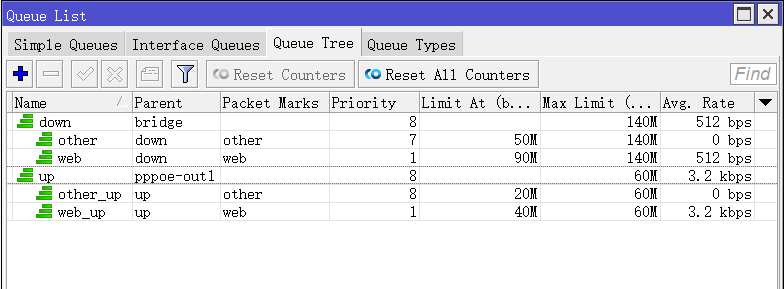
/queue tree add max-limit=140M name=down parent=bridge add max-limit=60M name=up parent=pppoe-out1web流量优先于其他流量priority设置1,其他流量priority优先级设置8,
/queue tree add max-limit=140M limit-at=90M name=web packet-mark=web parent=down priority=1 add max-limit=140M limit-at=50M name=other packet-mark=other parent=down priority=8 add max-limit=60M limit-at=40M name=web_up packet-mark=web parent=up priority=1 add max-limit=60M limit-at=20M name=other_up packet-mark=other parent=up priority=8
- down作为下行父级总带宽140M,子队列包含web和other,
- up作为上行父级总带宽60M,子队列包含web_up和other_up
- web:定义max-limit最大可以获取140M,limit-at为90M(保证最少带宽90M,其他子队列无法抢占),优先级1,即最高
- other:定义max-limit最大可以获取140M,limit-at为50M(保证最少带宽50M,其他子队列无法抢占),优先级8,最低
 下载的运行结果:
下载的运行结果:
- other流量达到140M时,web流量需求不断增加,other优先级低于web,会释放90M带宽给web,由于limit-at的设置保证了other保留50M带宽,这时web流量是90M,other流量是50M
- 当web流量达到140M时,other流量需求20M,虽然web优先级高于other,但limit-at要求最低保证50M带宽,因此web会释放20M给other,满足limit-at的需求。
基于IP的HTB
网络情况如上,假如网络中有两台主机需要进行优先级的设置,如192.168.88.8和192.168.88.9两台主机进行流量控制,要求192.168.88.8获取带宽优先级高于192.168.88.9。 首先在mangle标记两台主机的连接,并从连接提取数据包,192.168.88.8标记为host8,192.168.88.9标记为host9,配置如下:/ip firewall mangle add action=mark-connection chain=forward new-connection-mark=host8 passthrough=\ yes src-address=192.168.88.8 add action=mark-packet chain=forward connection-mark=host8 new-packet-mark=host8 \ passthrough=no add action=mark-connection chain=forward connection-mark=no-mark \ new-connection-mark=host9 passthrough=yes src-address=192.168.88.9 add action=mark-packet chain=forward connection-mark=host9 new-packet-mark=\ host9 passthrough=no在queue tree配置主机的HTB流控规则,host8优先级设置为1,host9优先级为7
/queue tree add max-limit=140M name=down parent=bridge add max-limit=140M limit-at=100M name=host8 packet-mark=host8 parent=down priority=1 add max-limit=140M limit-at=10M name=host9 packet-mark=host9 parent=down priority=7 add max-limit=60M name=up parent=pppoe-out1 add max-limit=60M name=host8_up packet-mark=host8 parent=up priority=1 add max-limit=60M name=host9_up packet-mark=host9 parent=up priority=7运行情况是host8优先级高于host9,如果host8和host9同时进行大流量下载数据,host8最大可以获得130M流量,因为host9的limit-at设置为10M,需要保证host9的最低带宽。

